Dove Prism
The Dove Prism is an important optical component widely used in optical systems due to its unique structure and optical properties, playing a crucial role in image rotation and beam deflection.
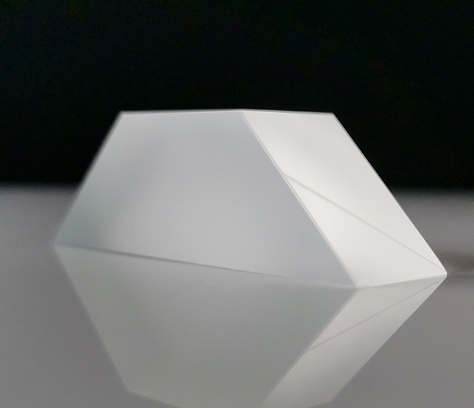

Structural Characteristics:
The Dove Prism is typically made of a rectangular glass block with parallel top and bottom surfaces and rectangular sides. Its key feature lies in the symmetrical base angles, enabling total internal reflection within the prism, thus altering the direction of light propagation. Through geometrical optics principles, one can analyze the structural features of the Dove Prism and study the transmission and deviation characteristics of incident light within its main section.
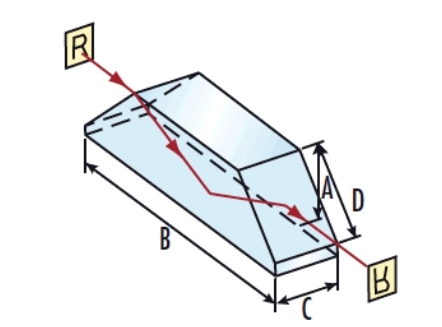
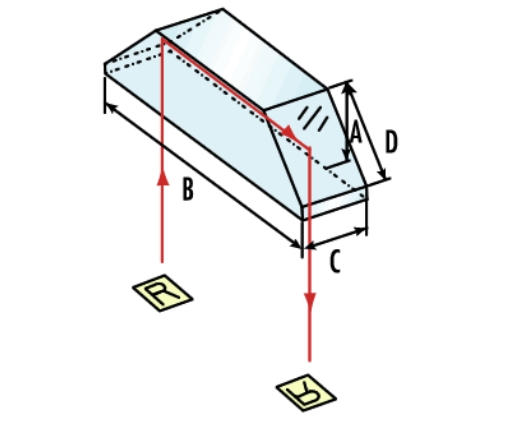
Working Principle:
The working principle of the Dove Prism is based on total internal reflection. When light enters one of the prism's side faces at a certain angle, it undergoes total internal reflection inside the prism and exits from the opposite side. Due to the prism's symmetric structure, the exiting light rotates relative to the incident light. Specifically, if the prism is rotated around its long axis, the exiting light rotates twice the angle.
Applications:
Image Rotation: Dove Prisms are commonly used for image rotation in optical systems. For instance, in microscopes, Dove Prisms can achieve a 180-degree image rotation, simplifying the mechanical design of the microscope.
Beam Deflection: In laser systems, Dove Prisms can alter the direction of beam propagation, facilitating precise control of the beam.
Fiber Optic Rotational Connectors: Dove Prisms also find important applications in fiber optic rotational connectors. Through the rotational properties of the Dove Prism, stable transmission of optical signals within the connector can be achieved.
Research Progress:
In recent years, with advancements in optical technology, research on Dove Prisms has made significant progress. For instance, utilizing optical design software like TracePro, virtual simulations have been conducted on the signal image transmission and rotation characteristics of Dove Prisms with different symmetrical base angles. Results indicate that Dove Prisms with varying symmetrical base angle structures can achieve signal image transmission and rotation functionalities.
As a vital optical component, the Dove Prism's unique structure and optical properties offer broad application prospects in numerous optical systems. Further optimization of its design and performance enhancement in practical applications can be achieved through in-depth research into its structural characteristics and working principles.

